Global Interconnect: Reusable Medical Connector Design Considerations

In this sponsored content post, the team at Global Interconnect share some tips on design considerations for reusable medical connectors. For single-use design considerations, click here.
Advanced Design and Selection of Reusable Medical Connectors
Creating and implementing reusable medical connectors in medical technology is a testament to innovation. These connectors, essential in various medical devices, demand advanced designs but also the utilization of premium materials and intricate manufacturing and validation processes.
Integration and Application of Reusable Connectors
Reusable connectors are ingeniously integrated either directly into the handpiece or through a full-length cable that seamlessly connects to the device and/or generator. Selecting the appropriate connector begins with a deep understanding of its specific application and how it will enhance the user experience for medical professionals, always prioritizing patient safety.

Determinants of Design and Material Choice
Key factors significantly influencing the design, material, and component selection include the connector’s cycle count and the chosen sterilization strategy. Sterilization methods vary, from Isopropyl wipes to hydrogen peroxide and heat or steam processes. Cycle counts can differ dramatically, from as few as 10 to as many as 10,000, depending on the sterilization technique employed.
Handling considerations, including storage, sterilization, daily use, and any potential patient risks are also vital when designing and manufacturing these connectors.
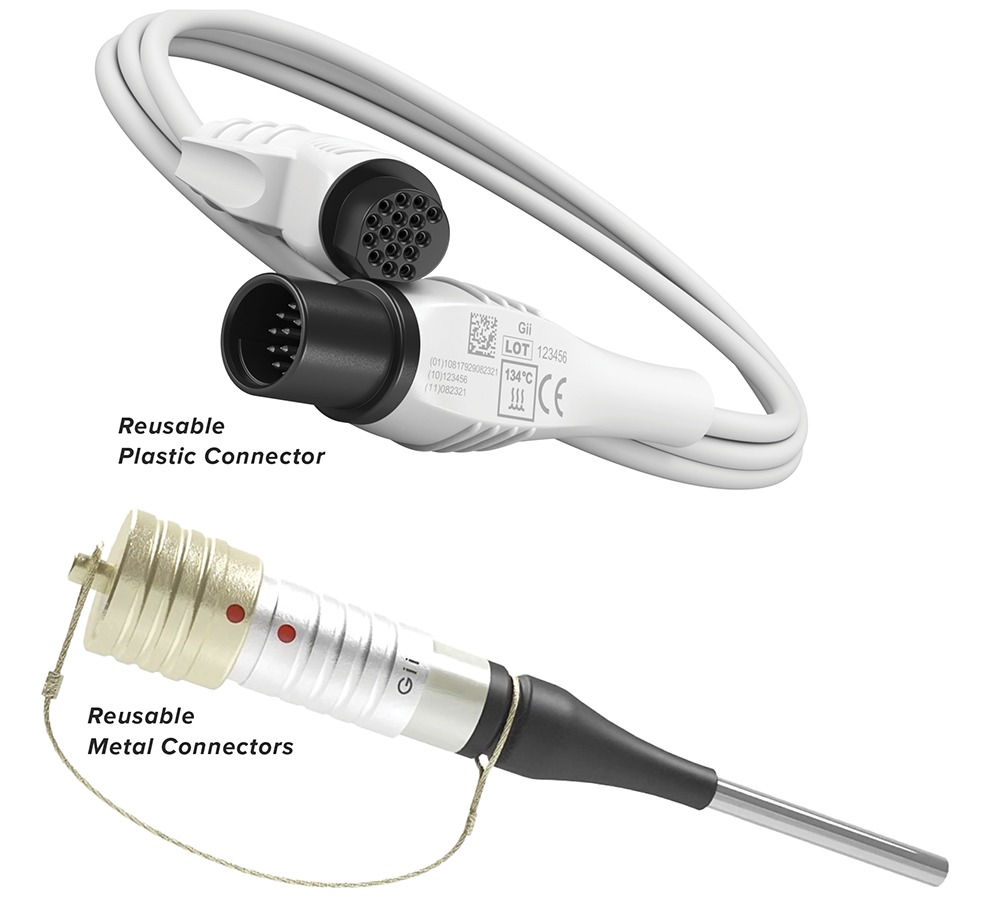
Essential Features of Reusable Medical Connectors
- Material Choices
- Plastic connectors, suitable for lower cycle counts (50-2000), offer a cost-effective solution. Ideal for simple wipe-down sterilization, they are frequently used in less intensive cycles (over 100).
- Common plastic types include PESU, PEI, and PSU, known for their patient safety benefits and reduced risk of electrical shock. However, prolonged exposure to heat and steam sterilization can compromise their integrity.
- Thanks to their durability, metal connectors are preferable for high-cycle uses (over 100) involving heat and steam sterilization.
- Mating Styles
- Non-locking connectors prevent damage and facilitate easy disconnection, reducing service requests.
- Breakaway connectors offer a more refined design and user experience, balancing higher insertion and extraction forces while minimizing failures.
- Locking connectors provide the most sophisticated design, preventing accidental disconnections during procedures.
- Contact Types
- Machined contacts with gold plating are ideal for high voltage, high density, and high cycle count reusable connectors.
- Edge cards (PCB style – FR4) are recommended for connectors with many electrical contacts; however, it’s crucial to consider sterilization and cycle counts.
- Options for pneumatic and fluidic contacts cater to specific needs like gas, saline, and suction handling.
- Fiber contacts are increasingly crucial for imaging and communication in emerging technologies.
Before finalizing a choice, weighing patient safety and performance requirements is imperative.
Global Interconnect, an ISO 13485 and FDA-registered contract manufacturing partner of energy-based devices with over three decades of experience, stands ready to assist medical device OEMs in finding their ideal reusable connector solution.
Global Interconnect is part of Chamfr’s Supplier Directory. They are an ISO 13485 and FDA-registered contract manufacturing partner of energy-based devices with over three decades of experience. They are ready to assist medical device OEMs in finding their ideal reusable connector solution. Engage with their team today and let them help you achieve immediate and long-term success.
Let’s keep in touch.
Don’t miss seller news, product alerts, and insights. Sign up for our emails to receive updates directly in your inbox.